5.3 Diamonds data
To demonstrate tools for large datasets, we’ll use the built in diamonds dataset, which consists of price and quality information for ~54,000 diamonds:
diamonds
#> # A tibble: 53,940 x 10
#> carat cut color clarity depth table price x y z
#> <dbl> <ord> <ord> <ord> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 0.23 Ideal E SI2 61.5 55 326 3.95 3.98 2.43
#> 2 0.21 Premium E SI1 59.8 61 326 3.89 3.84 2.31
#> 3 0.23 Good E VS1 56.9 65 327 4.05 4.07 2.31
#> 4 0.290 Premium I VS2 62.4 58 334 4.2 4.23 2.63
#> 5 0.31 Good J SI2 63.3 58 335 4.34 4.35 2.75
#> 6 0.24 Very Good J VVS2 62.8 57 336 3.94 3.96 2.48
#> # … with 53,934 more rowsThe data contains the four C’s of diamond quality: carat, cut, colour and clarity; and five physical measurements: depth, table, x, y and z, as described in Figure 5.1.
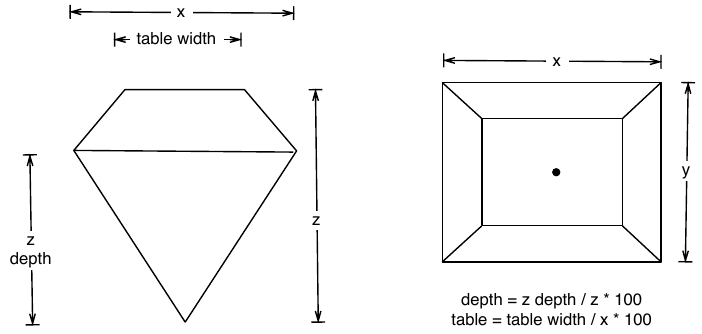
Figure 5.1: How the variables x, y, z, table and depth are measured.
The dataset has not been well cleaned, so as well as demonstrating interesting facts about diamonds, it also shows some data quality problems.